Dental implant infection, also known as peri-implantitis, is a serious condition that can affect the tissues and bone around a dental implant. It usually occurs when bacteria invade the implant site, causing inflammation. Common signs include pain, swelling, and bleeding gums. If untreated, it can lead to severe complications. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, and aftercare tips for dental implant infections.
Key Takeaways
- Dental implant infection, or peri-implantitis, can lead to severe complications if not identified and treated promptly, highlighting the importance of early recognition.
- Key risk factors for dental implant infections include poor dental hygiene, smoking, and underlying medical conditions, emphasizing the need for preventive measures.
- Treatment options range from antibiotics and mechanical cleaning to surgical interventions and implant removal, underscoring the necessity of individualized care based on infection severity.
Understanding Dental Implant Infection
Understanding these infections benefits anyone with a dental implant or those considering the procedure. Early recognition and prompt treatment can significantly impact the outcome, preserving both the implant and overall oral health.
Common Causes of Dental Implant Infections
Several factors can trigger dental implant infections, with poor dental hygiene being one of the most prevalent. Inadequate oral care leads to the accumulation of plaque and tartar, which can irritate the tissues around the implant and cause infections. Smoking is another major risk factor, as it impairs blood flow to the gums, hindering the healing process and making the tissues more susceptible to infection.
Medical conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes, previous gum disease, and weakened immune systems also heighten the risk of developing infections around dental implants. Recognizing these causes helps mitigate risks and ensure the success of dental implants.
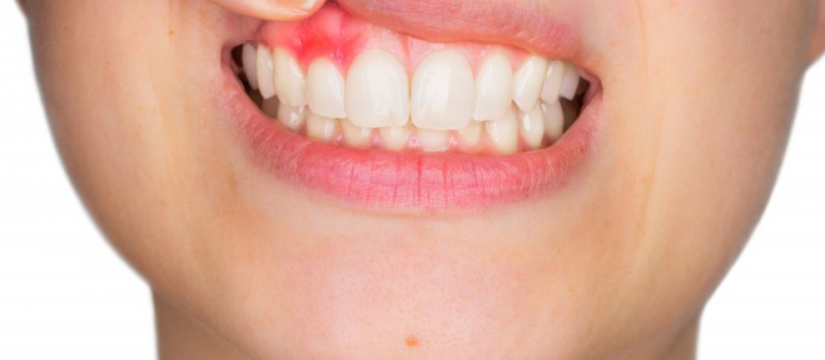
Recognizing the Symptoms of an Infected Dental Implant
Early identification of infected dental implant symptoms can prevent complications and increase the chances of successful treatment.
Common signs of a dental implant infection include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Bleeding gums
- A foul smell
- Loose implants
These symptoms can disrupt daily activities such as chewing and talking, highlighting the need for immediate attention.
Additional symptoms to watch out for include tender gums, increased pocket depth around the implant, and persistent bad breath. If any of these signs appear, seek treatment immediately to prevent the infection from worsening.
Diagnosing Dental Implant Infections
The process of diagnosing a dental implant infection typically begins with a dental x-ray, which helps in assessing the extent of the infection. Dentists may also gently probe the area around the implant to determine the degree of infection and identify any pockets of bacteria.
Symptoms such as persistent bleeding, fever, and swollen lymph nodes can also indicate a potential infection and should prompt a visit to the dentist. Accurate early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further complications.
 Treatment Options for Dental Implant Infections
Treatment Options for Dental Implant Infections
Treatment options for dental implant infections vary depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s condition. Early-stage infections can often be managed with non-surgical treatments such as antibiotics and modifications to the prosthetic design. For more advanced cases, mechanical cleaning techniques, surgical interventions, or even implant removal may be necessary.
Knowing these treatment methods enables patients to make informed decisions about their dental care. The following subsections provide a detailed look at each treatment option, from antibiotics to implant removal and bone grafting.
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotics are often the first line of defense against bacterial infections around dental implants. In cases of mild to moderate infection, antibiotics can effectively eradicate the bacteria and prevent the infection from spreading. Typically, a course of antibiotics is prescribed for at least two weeks, depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health.
Patients must complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed to fully treat the infection. In some cases, additional treatments may be necessary if the infection does not respond adequately to antibiotics alone.
Mechanical Cleaning Techniques
Carbon fiber curettes are advantageous because they minimize damage to the implant surface while effectively removing buildup. Regular mechanical cleaning maintains the health of dental implants and prevents further complications.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention may be required to address dental implant infections in some cases. This is especially true if the implant is incorrectly positioned or if non-surgical treatments are insufficient. Surgical procedures involve making flap-like incisions to access the contaminated areas, followed by mechanical cleaning and the application of antiseptics.
Moderate to advanced infections may require additional procedures like decontamination of the microimplant surface and bone regeneration techniques. LAPIP treatment is a less invasive option that can effectively treat infected implants in just one or two sessions, reducing the need for multiple painful procedures.
Implant Removal and Bone Grafting
In severe cases of infection or when an implant fails, removal of the implant may be necessary. This is often followed by a bone graft to rebuild lost tissue and prepare the site for future implants. Bone grafting involves the transplantation of bone tissue to the affected area, promoting new bone growth and providing a stable foundation for a new implant.
Though intensive, implant removal and bone grafting can be essential for restoring oral health and achieving successful outcomes with future dental implants.
Preventing Dental Implant Infections
Mechanical cleaning techniques are essential for managing dental implant infections. Tools such as ultrasonic devices and carbon fiber curettes are used to clean and disinfect the area around the implant. These instruments are particularly effective in removing plaque, tartar, and other debris that can harbor bacteria and cause infections.
Excellent oral hygiene and regular professional cleanings are the foundation for preventing dental implant infections. Proper brushing and flossing techniques remove plaque and bacteria that can lead to infections. Using a water flosser can also help clean between dental implants and natural teeth, reducing the risk of bacterial buildup.
Avoiding smoking is crucial, as it significantly increases the risk of implant infections and can hinder treatment success. Good oral hygiene and preventive measures allow patients to enjoy the benefits of dental implants without complications from infections.
The Importance of Aftercare Following Dental Implant Procedures

Avoiding strenuous activities and smoking for at least two weeks post-surgery minimizes complications. Gentle rinsing with a warm saltwater solution starting the day after surgery promotes healing and reduces the risk of infection.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures a smooth recovery and supports overall dental health and oral health.
When to Seek Emergency Dental Care

Though dental implant infections are generally not emergencies, worsening symptoms may require immediate attention. If you suspect an infection, contact your dentist immediately to address the issue and prevent further damage.
Choosing the Right Dentist for Dental Implant Infections
Choosing the right dentist to treat dental implant infections ensures successful outcomes. Thoroughly check the qualifications and credentials of potential specialists to ensure they have the appropriate training and licenses. Experience is crucial, so look for a dentist in Rockville, MD with a proven track record in dental implant surgeries.
Gather referrals from friends or family, read online reviews, and ensure the dentist provides clear explanations and reassurances about the procedures. A dentist committed to ongoing education in implant dentistry is likely to be well-versed in the latest techniques and technologies, which enhances the quality of care.
Summary
In summary, dental implant infections can be effectively managed with proper understanding, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment. By recognizing the causes and symptoms, maintaining excellent oral hygiene, and adhering to aftercare instructions, patients can prevent infections and ensure the longevity of their dental implants.
Choosing the right dentist and seeking prompt care when needed are also critical steps in managing dental implant health. Remember, proactive measures and informed decisions are key to enjoying a confident smile and maintaining overall oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can antibiotics clear up a dental implant infection?
Yes, antibiotics like tetracycline and metronidazole can be effective in treating localized dental implant infections. They can be applied topically or administered systemically to help clear the infection.
How do I know if my dental implant is infected?
You can identify a dental implant infection by observing increased swelling, redness, and potential fever. Additionally, an unusual persistent bad taste in your mouth may indicate a buildup of bacteria and debris around the implant.
What are the common causes of dental implant infections?
Dental implant infections are commonly caused by poor dental hygiene, smoking, uncontrolled diabetes, and a history of gum disease. Maintaining proper oral care and addressing these risk factors is crucial for implant success.
What symptoms indicate a dental implant infection?
Symptoms indicating a dental implant infection include pain, swelling, bleeding gums, and a foul smell, as well as persistent bad breath and loose implants. It is crucial to seek prompt medical attention if these symptoms arise.
How are dental implant infections diagnosed?
Dental implant infections are diagnosed through dental x-rays and probing around the implant, with additional consideration given to symptoms such as persistent bleeding and fever. Early identification through these methods is crucial for effective treatment.

 Treatment Options for Dental Implant Infections
Treatment Options for Dental Implant Infections