Sleep apnea, a common yet often unrecognized sleep disorder, can silently wreak havoc on a person’s daily life and overall health. Millions of people suffer from this condition, experiencing disrupted sleep, daytime fatigue, and an increased risk of serious health complications. So, how can you recognize the signs of sleep apnea and take steps to address it? In this blog post, we will provide a comprehensive guide to understanding, diagnosing, and treating sleep apnea, empowering you to take control of your sleep and well-being.
Through a deep dive into the two main types of sleep apnea – obstructive and central – we will explore the differences between these conditions and their implications for proper diagnosis and treatment. From identifying common and unique symptoms to examining risk factors and causes, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sleep apnea. So, let’s embark on this journey to better sleep and improved health together.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep Apnea is a sleep disorder that affects breathing during sleep and can lead to serious health issues.
- Symptoms of Sleep Apnea include snoring, gasping for air, excessive daytime fatigue and morning headaches.
- Treatment options range from non-invasive therapies to lifestyle changes such as weight loss, exercise and smoking cessation.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by abnormal breathing patterns during sleep and is one of the most common sleep disorders. There are two main types: obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. Grasping the differences between these types paves the way for accurate diagnosis and treatment. So, how is sleep apnea diagnosed and treated? Understanding the specifics of each type is crucial.
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when throat muscles relax, leading to airway narrowing or closure, causing brief awakenings and disrupted sleep. Central sleep apnea, on the other hand, is caused by a lack of signals from the brain to the breathing muscles, resulting in difficulty breathing and sleeping.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea, the more common of the two types, occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat relax during sleep, resulting in a reduced space for air to pass through. This leads to recurrent episodes of obstructed breathing during sleep, which can cause:
- decreased blood oxygen levels
- daytime sleepiness
- fatigue
- morning headaches
- difficulty concentrating
- irritability
- mood changes
- high blood pressure
- heart problems
Loud snoring, a frequent indicator of sleep apnea, is the result of the airway narrowing due to the relaxation of throat muscles during sleep.
As a result, those with obstructive sleep apnea may suffer from numerous awakenings throughout the night, frequently without their knowledge, culminating in subpar sleep quality and pronounced daytime drowsiness. Untreated obstructive sleep apnea can result in serious health issues, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea is a less common but equally concerning form of sleep apnea. Unlike its obstructive counterpart, central sleep apnea is characterized by a lack of signals from the brain to the breathing muscles, causing irregular breathing patterns during sleep. This can result in shallow respiration, interruptions in respiration, and excessive somnolence during the day.
The causes of central sleep apnea can vary widely and often involve underlying medical issues affecting the brain stem, heart, or kidneys. For example, congestive heart failure, hypothyroidism, and neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s can all contribute to the development of central sleep apnea.
Treatment for this type of sleep apnea typically focuses on resolving the medical issue causing abnormal breathing, but in some cases, additional therapies may be necessary to improve breathing and address the underlying problem.
Identifying Symptoms

Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnea can be challenging, as they often overlap between the two types and may not be easily noticeable. However, being aware of the common and unique symptoms of both obstructive and central sleep apnea can aid in proper diagnosis and treatment.
In the following sections, we will explore the distinct symptoms associated with each type of sleep apnea and provide insight into their potential causes and implications for your health.
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms shared by both types of sleep apnea include:
- Snoring: loud, harsh breathing during sleep
- Gasping for air: brief pauses in breathing during sleep that can disrupt sleep quality and result in daytime fatigue
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
These symptoms are often the most noticeable and widely recognized signs of sleep apnea.
Excessive daytime sleepiness is another common symptom that can significantly impact the lives of those with sleep apnea. This feeling of fatigue and drowsiness during the day can make it difficult to concentrate, stay alert, and perform daily tasks effectively.
Recognizing these prevalent symptoms and pursuing medical advice if you suspect sleep apnea is of utmost importance.
Unique Symptoms
While common symptoms can provide valuable clues to the presence of sleep apnea, unique symptoms may vary between individuals and can help further pinpoint the specific type of sleep apnea at play. Some of these unique symptoms may include morning headaches, irritability, and difficulty paying attention.
Morning headaches are a distinctive symptom of sleep apnea that can manifest when a person awakens in the morning, potentially due to poor sleep quality and disrupted oxygen levels. Irritability is another distinct symptom of sleep apnea that can present as a sensation of frustration or anger, while difficulty paying attention can manifest as trouble concentrating on activities or discussions.
Recognizing these unique symptoms and understanding their variance among individuals can contribute to the accurate diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea.
Risk Factors and Causes

Sleep apnea can affect anyone, but certain factors increase the risk for each type. Comprehending the risk factors and causes linked with both obstructive and central sleep apnea enables individuals to take measures to lessen their risk and pursue suitable treatment when required.
In the following sections, we will delve into the specific risk factors and causes for each type of sleep apnea, shedding light on the complexities of this sleep disorder.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Age, sex, body weight, and certain anatomical features of the head and neck are considered to be risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea. Changes in any of these can increase your chances of developing this condition. Here are some risk factors to be aware of:
- Age: As individuals age, their risk of developing sleep apnea increases.
- Sex: Men are more likely than women to develop the condition.
- Body weight: Excess body weight, particularly in the form of obesity, is another significant risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea. Excess fat deposits around the upper airway can obstruct normal airflow during sleep.
Additionally, certain anatomical features of the head and neck region can contribute to the development of obstructive sleep apnea. These may include a narrow airway, enlarged tonsils or adenoids, or a recessed chin, all of which can increase the likelihood of airway obstruction during sleep.
Recognizing these risk factors and tackling them when feasible can mitigate the risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea.
Central Sleep Apnea
Risk factors for central sleep apnea include:
- Underlying medical issues affecting the brain stem, heart, or kidneys
- Congestive heart failure
- Hypothyroidism
- Neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s
- Age (older individuals are more susceptible)
- Gender (males are more likely to develop the condition)
Appreciating the specific risk factors for central sleep apnea aids individuals and healthcare providers in identifying potential causes of the condition and formulating a suitable treatment plan. By addressing underlying medical issues and managing risk factors, individuals can reduce their risk of developing central sleep apnea and improve their overall health and well-being.
Diagnosing Sleep Apnea
Diagnosing sleep apnea involves a combination of consultation, physical examination, and sleep studies. Correct diagnosis is vital in deciding the suitable treatment plan, ensuring the best possible results for those living with sleep apnea.
In the following sections, we will discuss the steps involved in diagnosing sleep apnea and the tools healthcare providers use to make an informed diagnosis.
Consultation and Physical Exam
The initial step in diagnosing sleep apnea is a thorough consultation with a healthcare provider, during which they will review the individual’s symptoms, health history, and any potential risk factors. This information can help the provider determine if sleep apnea may be the cause of the individual’s sleep disturbances and guide further diagnostic steps.
Following the consultation, a physical exam is conducted to identify any signs of sleep apnea and recognize potential factors that could lead to the condition. During the physical exam, the healthcare provider may examine the individual’s head and neck region, checking for any anatomical abnormalities that could contribute to airway obstruction.
This holistic approach, merging consultation and physical examination, guarantees an exhaustive evaluation of the individual’s sleep health, assisting in identifying the presence of sleep apnea.
Sleep Studies
Sleep studies, like polysomnography, play a vital role in confirming the diagnosis of sleep apnea and ascertaining the specific type of sleep apnea present. Polysomnography involves the monitoring of several aspects of sleep, including:
- Breathing
- Awakenings
- Oxygen levels
- Muscle movement
- Sleep stages
This comprehensive sleep study, conducted by a sleep specialist, can provide valuable information to healthcare providers, helping them determine the best course of treatment for the individual and answering the question of how is sleep affecting their overall health.
Patients who are suspected to be suffering from more severe obstructive sleep apnea may have the option of an at-home sleep study. Such a study can provide accurate results without going to a clinic or health care center. However, polysomnography remains the most dependable type of sleep study, as it provides a complete picture of an individual’s sleep health and can accurately diagnose both obstructive and central sleep apnea.
Treatment Options
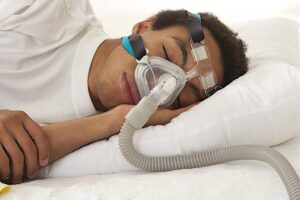
Various treatment options are available for sleep apnea, depending on the type, severity, and individual needs of the patient. These options include:
- Non-invasive treatments
- Surgical procedures
- Lifestyle modifications
- Continuous self-care
People with sleep apnea have an array of resources and alternatives to manage their condition and enhance their quality of life.
In the following sections, we will explore the different treatment options available and discuss their benefits and limitations.
Non-Invasive Treatments
Non-invasive treatments to treat sleep apnea include positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy, oral appliances, and oxygen therapy. PAP therapy, often in the form of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices, is a common and effective treatment option for individuals with obstructive sleep apnea. With sleep apnea treated by this therapy, it works by increasing the air pressure inside the airway and lungs during inhalation, preventing the surrounding tissue from obstructing the airway.
Oral appliances, prescribed by dentists and sleep medicine specialists, can help maintain the position of the jaw and tongue, relieving pressure on the airway and reducing the risk of obstruction.
Oxygen therapy, on the other hand, involves the administration of supplemental oxygen during sleep, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with central sleep apnea or those who experience drops in oxygen levels during sleep.
Surgical Treatments
In some cases, surgical treatments may be considered for those who do not respond to non-invasive treatments or have severe anatomical issues contributing to their sleep apnea. Surgical options for sleep apnea include:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), which involves the removal of excess tissue from the throat to expand the airway
- Tracheostomy, a procedure in which a hole is created in the windpipe to bypass an obstructed airway
- Nasal surgeries, which can improve airflow through the nose
For some individuals, weight loss surgeries may also be a viable option, particularly if obesity is a significant contributing factor to their sleep apnea. By addressing the underlying anatomical issues and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with sleep apnea can explore the most appropriate surgical treatments for their specific needs and circumstances.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing sleep apnea symptoms and reducing risk factors associated with the condition. Some effective lifestyle changes include:
- Weight loss
- Regular exercise
- Cessation of smoking and alcohol consumption
- Alterations to sleep position
These changes can contribute to improved sleep quality and reduced symptoms of sleep apnea.
Utilizing a humidifier, avoiding certain medications, and wearing an oral appliance at night may also provide relief for individuals with sleep apnea. Implementing these lifestyle modifications can not only diminish the severity of sleep apnea symptoms but also enhance overall health and well-being, making them an essential component of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Living with Sleep Apnea
Living with sleep apnea requires ongoing self-care and support to ensure optimal health and well-being. Individuals with sleep apnea can considerably enhance their quality of life and lower the risk of complications associated with the condition by complying with prescribed treatment plans, monitoring symptoms, and fostering a healthy lifestyle.
In the following sections, we will discuss effective self-care strategies and the available support and resources to help individuals manage their sleep apnea and live their lives to the fullest.
Self-Care Strategies
Compliance with treatment plans, as prescribed by a doctor, forms a vital part of self-care for individuals with sleep apnea. This may include taking medications, using a CPAP machine, or undergoing surgery as needed. By following their prescribed treatment plans, individuals with sleep apnea can effectively manage their condition and maintain their overall health and well-being.
In addition to adhering to treatment plans, monitoring symptoms and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential self-care strategies for individuals with sleep apnea. Here are some self-care strategies to consider:
- Observing snoring, daytime sleepiness, and difficulty concentrating can help individuals recognize changes in their condition and seek medical advice when necessary.
- Engaging in regular physical activity can contribute to improved sleep quality.
- Consuming a nutritious diet can support overall health and well-being.
- Refraining from alcohol and tobacco consumption can help reduce sleep apnea symptoms.
By incorporating these self-care strategies into your routine, you can improve your sleep quality and manage your sleep apnea more effectively.
Support and Resources

Support and resources are available through healthcare providers, sleep specialists, and sleep apnea support groups to help individuals manage their condition and improve their quality of life. These resources can provide invaluable guidance, advice, and emotional support for those living with sleep apnea, helping them navigate the challenges and successes of their treatment journey.
Organizations such as the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, American Sleep Apnea Association, and National Sleep Foundation offer additional assistance and resources to individuals with sleep apnea, including educational materials, support groups, and advocacy efforts. By taking advantage of these support systems and resources, individuals with sleep apnea can feel empowered to take control of their condition and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Summary
In conclusion, sleep apnea is a common but often unrecognized sleep disorder that can have serious implications for an individual’s daily life and overall health. By understanding the differences between the two main types of sleep apnea – obstructive and central – and recognizing the signs, symptoms, and risk factors associated with each type, individuals can take steps to address their condition and improve their quality of sleep.
Through comprehensive diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing self-care and support, those living with sleep apnea can effectively manage their condition and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. A dentist in rockville md can be an integral part of your care team, offering specialized treatments for sleep apnea. Remember, sleep is a vital component of overall health and well-being, and addressing sleep apnea is an essential step toward achieving restorative sleep and a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 3 symptoms of sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea symptoms include abnormal breathing patterns, excessive daytime sleepiness, nighttime awakenings, sudden shortness of breath or chest pains at night, difficulty focusing, morning headaches, loud snoring, observed episodes of stopped breathing during sleep, waking during the night and gasping or choking, awakening in the morning with a dry mouth or sore throat, trouble focusing during the day, and mood changes.
What is sleep apnea caused from?
Sleep apnea is caused by either a blockage of the airway (obstructive sleep apnea), or by the brain not sending the signals needed to breathe (central sleep apnea). Obstructive sleep apnea can be caused by excess weight, large tonsils, and changes in hormone levels. Central sleep apnea may result from existing conditions like heart failure and stroke, as well as sleeping at a high altitude.
How do you fix sleep apnea?
Treatment for sleep apnea may include lifestyle changes, CPAP machines, oral appliances, nerve stimulators, surgery, medications, or a combination of these. The most commonly recommended and effective treatment is a CPAP machine which delivers just enough air pressure to a mask to keep the upper airway passages open, preventing snoring and sleep apnea.
Is sleep apnea very serious?
Sleep apnea is very serious, as it can lead to difficulty concentrating, decisions, and remembering, and increase the risk of long-term health complications or even death. It is also linked to heart damage and heart failure, making it a potentially life-threatening condition.
What is the difference between obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when throat muscles relax, leading to airway narrowing or closure, whereas central sleep apnea is caused by a lack of signals from the brain to the breathing muscles, causing difficulty in breathing and sleeping.








