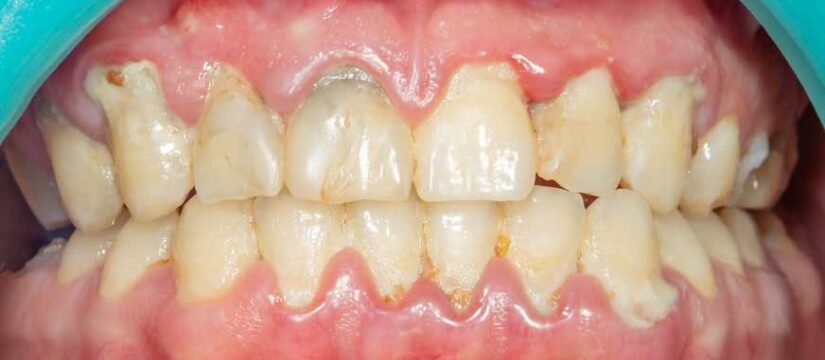
Did you know that maintaining your oral health is about more than just preserving a beautiful smile? Periodontitis, a severe gum infection, can lead to tooth loss and other health complications if left untreated. In this blog post, you’ll discover the symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention strategies for periodontitis, empowering you to take charge of your oral health and overall well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Periodontitis is a serious condition and understanding its symptoms, causes, treatments, and home remedies can help prevent it.
- Early warning signs include bleeding gums, gum recession and pockets between teeth & gums – prompt action is necessary to stop progression of the disease.
- Regular dental cleanings are essential for maintaining oral health & preventing periodontitis which can have long term effects on overall health.
Understanding Periodontitis
Periodontitis, often referred to as gum disease or periodontal disease, is a severe gum infection that threatens not only your teeth but also your overall health. When left untreated, this condition can result in lost gum tissue, diseased gum tissue, loose teeth, and an increased risk of stroke, heart attack, and other health issues. Unfortunately, advanced gum disease is not curable; however, it can be managed with the right gum disease treatment, which may include bone grafts in some cases.
Familiarizing yourself with the symptoms, causes, and treatments of periodontitis can aid in preserving good oral health and halting the advancement of this condition. By recognizing the early signs and adopting proper oral hygiene practices, you can minimize the risk of developing periodontal disease and its associated complications.
Recognizing Symptoms
Early intervention and treatment of periodontitis can impede the advancement of the disease and avert additional harm, helping to maintain healthy gum tissue.
Identifying the symptoms of periodontitis enables you to proactively address the condition, thereby preserving your oral health.
Early Warning Signs
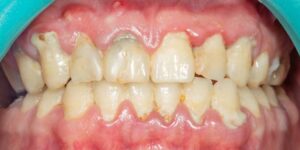
The initial indications of periodontitis include bleeding gums, gum recession, and pockets between teeth and gums. At this stage, the gum disease is called gingivitis, and if treated early, it is possible to reverse the condition through consistent dental cleaning and conscientious oral hygiene. These pockets between the teeth and gums harbor harmful bacteria, which, if left untreated, can lead to the progression of periodontitis.
Paying close attention to these preliminary warning signs and seeking dental advice upon noticing any changes in your gum health, especially near the gum line, is highly advisable. Prompt action can thwart the progression of more severe periodontal disease, facilitating the preservation of healthy gum tissue.
Progression of Symptoms
As periodontitis progresses, the symptoms become more severe. Moderate periodontal disease is characterized by bleeding and pain around the teeth, gum recession, loose teeth, and inflammatory response throughout the body. In advanced periodontitis, patients may experience intense discomfort while chewing, intense halitosis, and a disagreeable taste in the mouth, as well as tooth loss.
Acknowledging the progression of symptoms is key in pursuing timely treatment, which can prevent further damage to your gums, teeth, and overall health. If you notice any of these more severe symptoms, consult your dentist or periodontist for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment plan.
Causes and Risk Factors
Grasping the causes and risk factors of periodontitis enables proactive prevention and more effective management of the condition.
Harmful Bacteria
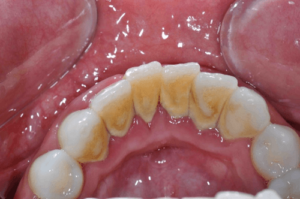
The primary cause of periodontitis is the presence of harmful bacteria in dental plaque, which can lead to inflammation and damage to gum tissue and bone. Bacteria such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, and Treponema denticola are found in dental plaque and are known to cause periodontal disease. These harmful bacteria secrete toxins that lead to inflammation and consequent destruction of the gums and bone which support the teeth.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits can limit the presence of these harmful bacteria in your mouth, thereby mitigating the risk of periodontitis.
Lifestyle and Health Factors
In addition to harmful bacteria, several lifestyle and health factors can increase your risk of developing periodontitis. These gum disease risk factors include:
- Smoking: Smoking adversely affects the gums and diminishes the body’s capacity to combat infection.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to develop periodontitis due to their impaired immune system and augmented levels of sugar in the saliva.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to periodontitis.
Managing these lifestyle and health factors can substantially lower your chances of developing periodontitis and help sustain good oral health.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Proper diagnosis and assessment by a dentist or periodontist are essential for determining the severity of periodontitis and creating an appropriate treatment plan. Periodontitis is diagnosed through a combination of methods, including:
- Reviewing medical history
- Conducting a clinical examination
- Performing periodontal probing
- Taking dental x-rays
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for evaluating the advancement of the disease and suggesting additional treatment options.
If you suspect you may have periodontitis, it’s advisable to seek dental consultation and come prepared with a list of queries for your appointment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and maintain your oral health.
Non-Surgical Treatments
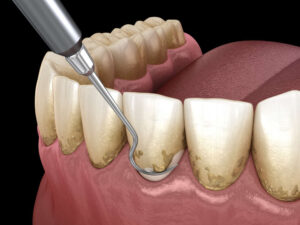
Non-surgical treatments for periodontitis may include professional dental cleanings, scaling and root planing, as well as medicated mouthwashes. Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical treatment that involves the removal of plaque and calculus in order to restore periodontal health. This procedure is often performed under local anesthesia to prevent any discomfort.
Other non-surgical treatments, such as medicated mouthwashes and professional dental cleanings, can also play a significant role in managing periodontitis. Adhering to your dentist’s advice for non-surgical treatments can ensure effective management of your periodontal health and prevent additional damage to your gums and teeth.
Surgical Interventions
In more severe cases of periodontitis, surgical interventions like flap surgery and bone grafting may be required to remove deposits beneath the gums and restore lost bone. The objective of these treatments, including the use of a bone graft, is to comprehensively clean the pockets around teeth and avert harm to adjoining gum tissue and bone loss. It’s essential to maintain a consistent regimen of good oral care during and after these treatments to maximize the chances of a successful outcome.
Surgical interventions can be highly effective in treating advanced periodontitis, but they should only be considered when non-surgical treatments have not been successful in managing the disease. Always consult with your dentist or periodontist to determine the best course of treatment for your specific case.
Home Remedies and Prevention
Adopting home remedies and prevention strategies can help you maintain good oral health and reduce the risk of periodontitis.
Oral Hygiene Tools
Using oral hygiene tools like:
- Toothbrushes
- Dental floss
- Water flossers
- Mouthwashes
can help prevent plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Brushing with toothpaste eliminates plaque and food particles from the teeth and gums, while interdental brushes clean the spaces between teeth and eradicate plaque and food debris from difficult-to-reach areas. Meanwhile, water pick (oral irrigator) and mouthwash work together to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth and gums, eliminating bacteria and diminishing plaque accumulation.
Adopting these oral hygiene tools as part of your daily routine can drastically decrease your chances of developing periodontitis, thus promoting a healthy and beautiful smile.
Regular Dental Cleanings
Regular dental cleanings and check-ups are essential for early detection and treatment of periodontitis. Dental cleanings should be undertaken every three to four months to avert periodontitis. During a dental cleaning, the dentist or hygienist will use specific tools to eliminate plaque and tartar from the teeth and gums and may also employ an ultrasonic scaler to remove any hard deposits.
After a dental cleaning, you may experience some slight discomfort, including tenderness or soreness. Your dentist may also suggest a fluoride treatment to aid in shielding your teeth from further harm.
Routine dental cleanings and check-ups, performed by a dental hygienist, are fundamental in preserving your oral health and warding off periodontitis.
The Connection Between Periodontitis and Overall Health
Comprehending the link between periodontitis and overall health is critical, given that untreated periodontal disease can escalate the risk of heart disease and other complications. Research has demonstrated correlations between gum disease and systemic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Inflammation associated with gum disease has also been linked to an augmented risk for heart disease and hypertension.
Managing periodontitis and upholding good oral health can substantially lessen your chances of encountering these systemic health issues, thereby enhancing your overall well-being.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding periodontitis, its symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention strategies is essential for maintaining good oral health and overall well-being. By recognizing early warning signs, adopting proper oral hygiene practices, and seeking timely interventions from dental professionals, you can effectively manage periodontitis and prevent the progression of this severe gum infection. Don’t let periodontitis jeopardize your health – take action today to protect your smile and your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can periodontitis be cured?
Unfortunately, periodontitis cannot be cured once it has progressed. However, it can be managed with proper oral hygiene, regular dental cleanings and special treatments such as scaling and root planing.
What are the 4 signs of periodontal disease?
The four signs of periodontal disease are swollen and tender gums, bad breath, receding gums and loose teeth.
Can teeth recover from periodontitis?
Periodontitis can be managed with appropriate treatment and good oral hygiene, but it cannot be cured. Early to moderate periodontal disease can take about 2 to 3 weeks to heal with the proper interventions like scaling and root planing, while severe cases may take 5 to 8 weeks. Despite some recovery of bone and tissue structure possible, it is not usually possible to get back all of the lost structural support.
What triggers periodontitis?
Poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque buildup are the main triggers for periodontitis. This infection of the tissues holding your teeth in place can lead to swollen, red, and bleeding gums.
What is the main difference between gingivitis and periodontitis?
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, while periodontitis occurs when the infection spreads to the bone and supporting tissues, potentially leading to tissue loss.