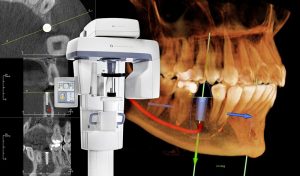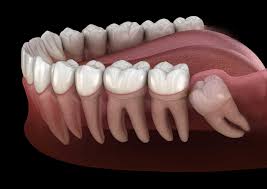
Have you ever wondered what sets oral surgeons apart from general dentists? Their highly specialized skills, rigorous training, and the unique services they provide make them indispensable in the world of dental care. In this blog post, we’ll explore the fascinating world of oral surgery, the role of an oral surgeon, and the incredible procedures they perform to help patients maintain optimal oral health.
Key Takeaways
- Oral surgeons are highly-qualified professionals providing comprehensive oral health care through specialized procedures.
- Patients should understand the differences between oral surgeons and general dentists to know when to seek treatment from an oral surgeon, as they possess a broader scope of practice.
- By following preoperative instructions, managing medications properly and understanding postoperative care guidelines, patients can ensure successful recovery from their surgery appointment.
The Role of Oral Surgeons in Dental Care
Oral surgeons are the superheroes of the dental world, possessing specialized knowledge and expertise that goes beyond the scope of general dentistry. These professionals are trained to perform advanced dental procedures such as wisdom teeth removal, dental implants, and the treatment of facial injuries. As part of a team of specialists, they provide comprehensive oral health care to ensure the highest quality of care for a range of dental concerns.
An oral surgeon’s qualifications are truly impressive, as they must complete dental school, a dental surgery residency program, and pass a board certification exam. This extensive training equips them to handle complex cases and provide the best possible outcomes for their patients. Next, we will examine more closely the specific procedures performed by oral surgeons, and the motivations behind them.
Wisdom Teeth Removal
Wisdom teeth removal is a common procedure performed by oral surgeons to prevent complications and ensure overall oral health. Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of teeth to develop and often lack the room to grow properly. This can lead to:
- Impacted teeth
- Pain
- Oral infections
- Other dental issues
The wisdom tooth extraction procedure involves making surgical incisions, removing the impacted teeth, and suturing the extraction site closed to facilitate healing. It is typically an outpatient procedure, with full recovery expected within a few days. In some cases, dentists may recommend wisdom teeth removal as a preventative measure even in the absence of impacted teeth.
Dental Implants
Another common procedure performed by oral surgeons is the placement of dental implants. Dental implants are a form of prosthetic tooth replacement, used to replace the root or roots of a tooth. They provide a permanent solution for missing teeth due to:
- decay
- disease
- oral cancer
- smoking
- alcoholism
The process for dental implants can involve a dental bone graft to restore volume and density in the jawbone, followed by the attachment of tooth restorations, such as crowns or bridges. Dental implants are constructed from medical-grade titanium or zirconia, ensuring durability and compatibility with the human body.
Treatment of Facial Injuries
Oral surgeons also play a vital role in treating facial injuries, including:
- Fractures
- Soft tissue injuries
- Nasal fractures
- Jaw fractures
- Cheekbone fractures
- Orbital fractures
They possess the expertise to handle a wide range of cases.
In addition to treating fractures, oral surgeons are skilled in addressing congenital conditions such as cleft lip and palate. This condition results from incomplete development of the facial structures in the uterus and requires specialized surgical intervention to correct.
The diverse range of procedures performed by oral surgeons showcases their exceptional skills and the essential role they play in dental care.
The Path to Becoming an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
The journey to becoming an oral and maxillofacial surgeon is both demanding and rewarding. These professionals undergo a rigorous educational and training process that includes dental school, a surgical residency, and board certification. This comprehensive training ensures that oral surgeons are equipped with the necessary skills and expertise to provide the highest level of care for their patients.
Throughout their education, oral surgeons gain a solid foundation in general dentistry and specialized knowledge in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Next, we will examine in detail the various stages of their education and training.
Dental School
Dental school is the first step on the path to becoming an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. It provides the groundwork for oral surgery, with an emphasis on general dentistry. The curriculum typically includes two years of biological science classes and two years of clinical work, ensuring a well-rounded education in the field of dentistry.
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons possess additional training and education beyond what is expected for dentists. Obtaining an MD degree can be added to a surgical diploma. It enables the individual to practice oral surgery with greater knowledge and expertise. They usually receive at least four years of training as a part of a hospital-based surgical program. The program provides an opportunity for medical residents from different specialties such as anesthesia, to gain comprehensive experience. This additional training sets oral surgeons apart from their general dentistry counterparts.
Surgical Residency
After dental school, aspiring oral surgeons continue their education with a surgical residency. This postgraduate training program provides comprehensive, hands-on experience in various medical specialties, preparing individuals for successful practice in oral surgery. The curriculum of a surgical residency typically includes rotations in:
- General surgery
- Trauma and critical care
- Pediatric surgery
- Specialized surgical rotations such as vascular, transplant, and reconstructive surgery
The surgical residency experience offers numerous advantages, including:
- The opportunity to gain hands-on experience in a variety of medical specialties
- Building a strong foundation in surgical techniques
- Learning how to manage complex medical cases
- Working with experienced surgeons and gaining valuable insight into the field of oral surgery
By completing a surgical residency, residents become well-prepared for a successful career in this specialized field.
Board Certification
Board certification is the final step on the path to becoming an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. This process ensures that these professionals meet rigorous standards of care and expertise. To obtain board certification, oral surgeons must complete the necessary training and educational requirements, followed by passing a specialty-specific examination to demonstrate medical knowledge, clinical skills, and diagnostic abilities.
Upon successful completion of their training, oral surgeons can become board-certified by the American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (ABOMS), which is the sole certifying board recognized by the American Dental Association for the specialty of oral and maxillofacial surgery in the United States. Board-certified oral surgeons must take part in the Certification Maintenance program every year to prove their current professional skills. This is a requirement of their profession.
Differentiating Between Oral Surgeons and General Dentists
Now that we’ve explored the educational journey and qualifications of oral surgeons, it’s essential to understand the differences between oral surgeons and general dentists. While both professionals play crucial roles in dental care, they differ in their areas of expertise, scope of practice, and when patients should seek treatment.
Next, we will examine more closely the differences between these dental professionals, which will help you understand when to seek treatment from an oral surgeon and the unique services they provide.
Areas of Expertise
The areas of expertise for oral surgeons and general dentists vary significantly, with oral surgeons often focusing on oral pathology and other specialized treatments.
Oral surgeons are trained to:
- Perform complex dental procedures, such as bone grafts
- Diagnose and treat diseases and injuries of the oral and maxillofacial regions
- Perform any type of surgery associated with the face
In contrast, general dentists focus on routine dental care, such as cleanings, fillings, and basic tooth extractions. While general dentists possess a breadth of knowledge in dental care, they do not have the advanced training and hands-on experience that oral surgeons gain through their surgical residencies.
Scope of Practice
The scope of practice for oral surgeons and general dentists also differs. Oral surgeons are equipped to handle more complex procedures and treat patients with medical conditions that require special care, such as dental implants or treatment for facial pain. They specialize in the diagnosis, surgical, and adjunctive treatment of diseases, injuries, and conditions related to the face, mouth, jaw, and oral cavity.
On the other hand, general dentists primarily focus on preventive care and the diagnosis and treatment of common dental problems. While they may perform some minor oral surgery procedures, their scope of practice is generally limited compared to that of oral surgeons.
When to Seek Treatment
Knowing when to seek treatment from an oral surgeon is crucial for ensuring the best possible outcome for your dental health. Your dentist may have recommended maxillofacial surgery, which is a dental specialty that focuses on the face and jaws. Such surgeries are performed to correct deformities and injuries of the face and jaw area. This type of surgery is used to address diseases and injuries that affect the areas surrounding the mouth.
A dentist may refer a patient to an oral surgeon if they are unable to provide the necessary treatment or if they deem an oral surgeon more suitable for the particular case. If you are experiencing complex dental concerns or have been referred by your dentist, consulting with an oral surgeon can provide you with the specialized care you need for a successful outcome.
Common Oral Surgery Procedures
Now that we have a better understanding of the role of oral surgeons and how they differ from general dentists, let’s explore some of the most common oral surgery procedures they perform. These procedures are essential for addressing a variety of dental concerns and ensuring the best possible outcomes for overall oral health.
Next, we will discuss tooth extractions, bone grafts, and orthognathic surgery, providing insight into the reasons for these procedures and what to expect during each process.
Tooth Extractions
Tooth extractions are a common oral surgery procedure performed by oral surgeons for various reasons, such as impacted teeth, overcrowding, or to facilitate orthodontic treatment. In some cases, a tooth extraction may be necessary due to severe tooth decay, gum disease, or dental trauma.
The tooth extraction procedure involves several steps:
- Numbing the tooth
- Extracting it with forceps
- Controlling bleeding
- Closing the gap left by the tooth
The jawbone and gum tissue will heal over time, with new bone and tissue filling the gap. Adhering to post-operative care instructions is crucial for ensuring a smooth recovery and minimizing the risk of complications.
Bone Grafts
Bone grafts are another common oral surgery procedure that helps to rebuild and strengthen the jawbone, often in preparation for dental implants. These procedures are essential for patients who have experienced bone loss due to tooth loss or other dental issues.
During a bone graft procedure, the surgeon makes an incision over the bone defect and inserts the bone graft in the designated area to augment the bone volume and stimulate healing. The incision in the gums should heal within a few weeks, and the bone graft will provide a solid foundation for dental implants or other restorative procedures.
Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery is a specialized oral surgery procedure designed to correct irregularities of the jaw bones. This type of surgery is often recommended for patients experiencing jaw misalignment, which can lead to issues with chewing, speaking, and overall oral function.
During orthognathic surgery, the oral surgeon will realign the jaw bones and secure them in their new position. This procedure can significantly improve a patient’s overall oral function and appearance, providing long-lasting benefits and an enhanced quality of life.
Anesthesia Options for Oral Surgery
Anesthesia plays a critical role in ensuring patient comfort and safety during oral surgery procedures. Various anesthesia options are available for oral surgery, each with its own benefits and indications. Next, we’ll examine local anesthesia, IV sedation, and general anesthesia, offering insight into the appropriate scenarios for each type of anesthesia and what to anticipate during the process.
Understanding your anesthesia options and discussing them with your oral surgeon can help you make an informed decision about the most suitable type of anesthesia for your procedure.
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is a type of anesthesia that numbs a particular region of the body, allowing patients to remain awake and comfortable during the procedure. It is commonly used for minor procedures, such as:
- tooth extractions
- skin biopsies
- mole removals
- joint injections
- minor surgeries
The process involves administering a local anesthetic, typically in the form of a topical application or injection, to numb the specific area of the body.
This type of anesthesia provides effective pain relief and has a lower risk of complications compared to other anesthesia options.
IV Sedation
IV sedation is a type of anesthesia that is administered intravenously, providing a deeper level of relaxation for patients during dental procedures. This form of sedation involves the delivery of an anti-anxiety drug through a tube placed in a vein, which is then administered directly into the bloodstream via an intravenous drip. This allows the patient to enter into a relaxed and semi-awake state, ensuring their comfort during more intricate procedures, such as dental implants.
IV sedation is a popular choice for patients who require a more profound level of relaxation and wish to be less aware of their environment during the procedure.
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia is a type of anesthesia that is delivered through inhalation and is used to induce a state of unconsciousness during the procedure. This form of anesthesia is typically reserved for more invasive procedures, such as orthognathic surgery, where the patient’s comfort and safety are paramount.
General anesthesia ensures that patients experience no pain or discomfort during surgery and allows the oral surgeon to perform complex procedures without causing distress to the patient. It is important to discuss any potential risks with your dentist or oral surgeon prior to undergoing general anesthesia.
How to Prepare for Your Oral Surgery Appointment
Preparing for your oral surgery appointment is an essential part of ensuring a successful outcome and smooth recovery. Following pre-operative instructions, managing medications, and understanding post-operative care are crucial steps in the preparation process.
Next, we will discuss specific pre-operative instructions, medication management, and post-operative care guidelines. This will help you feel confident and prepared for your oral surgery appointment.
Pre-Operative Instructions
Adhering to your doctor’s pre-operative instructions is crucial for ensuring patient safety and achieving optimal surgical outcomes. These instructions may include dietary restrictions, medication guidelines, and other activities to avoid prior to surgery. Make sure to inform your doctor of any medications you are taking, including over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements, as this information can impact your surgical plan.
By following these guidelines, you can set the stage for a successful surgical procedure and a smooth recovery.
Medication Management
Managing your medications is an essential aspect of preparing for oral surgery. It is crucial to inform your physician about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements, as they may affect your surgical plan or interact with medications prescribed for post-operative care.
Your physician may prescribe antibiotics or other medications to be taken prior to surgery, and it is important to follow their instructions carefully. In some cases, you may need to avoid certain medications, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, prior to surgery to minimize the risk of complications.
Post-Operative Care
Post-operative care is a vital component of recovering from oral surgery. Following your doctor’s instructions for post-operative care can help ensure a successful recovery and minimize the risk of complications. Here are some important steps to take:
- Take medications as prescribed.
- Adhere to any dietary restrictions.
- Refrain from strenuous activities.
- Attend your follow-up appointments.
- Contact your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms.
By following these steps, you can promote healing and ensure a smooth recovery process.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can promote healing and get back to your normal activities as soon as possible.
Summary
Oral surgeons play a critical role in dental care, performing complex procedures and addressing issues that go beyond the scope of general dentistry. Their specialized training, expertise, and dedication to patient care make them invaluable in maintaining optimal oral health. Whether you’re facing wisdom tooth removal, dental implant placement, or orthognathic surgery, an oral surgeon can provide the advanced care you need for a successful outcome. Now that you have a deeper understanding of the world of oral surgery and the professionals who make it possible, you can confidently seek treatment and navigate the path to a healthier, happier smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is difference between oral surgeon and dentist?
Oral surgeons are specialists who receive specialized training to perform a variety of complicated surgeries, including tooth extractions, dental implants, and facial procedures, while general dentists are trained in more basic restorative, surgical and cosmetic dentistry procedures. Oral surgeons have completed all the training required to become a dentist and then gone on to specialize in surgery.
What is the difference between oral surgery and oral and maxillofacial surgery?
Oral surgery is primarily concerned with the treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, while oral and maxillofacial surgery covers a wider range of treatments within and beyond the mouth, including facial reconstruction and jaw realignment. Maxillofacial surgeons are also able to specialize further into specializations like orthognathic and cleft palate surgery.
Are you put to sleep for oral surgery?
Not all the time but for complicated cases you will be put to sleep for oral surgery. The dentist typically needs to anesthetize the patient in order for them to not feel any discomfort or pain during the procedure.
When should I seek treatment from an oral surgeon?
If you have complex dental concerns, or if your general dentist refers you for treatment beyond their scope of care, it is recommended to seek treatment from an oral surgeon.
What are some common oral surgery procedures?
Common oral surgery procedures include wisdom teeth removal, dental implants, and orthognathic surgery.